Abstract
Introduction: There are knowledge gaps regarding splenic infarcts (SI), given the heterogenic patient population and wide range of clinical presentation. Comprehensive data on the frequency, management and outcomes of cryptogenic SI are lacking.
Aim: To assess the etiology, treatment patterns and outcome of patients with SI, with an emphasis on cryptogenic SI.
Methods: Single-center retrospective cohort study including adults with acute symptomatic or incidental SI. Patients were indexed at SI diagnosis and records were followed for 12 months. Patients were identified by ICD-9 diagnoses and an electronic search of the text in all radiology reports, and confirmed by manual review. Thrombotic risk-factors were classified as "baseline" if known at index or as "newly-diagnosed" if identified in diagnostic tests that were performed or recommended during hospitalization for the index SI. Diagnostic work-up was performed according to the clinician's discretion.
The clinical context as well as baseline and newly-diagnosed thrombotic risk factors were used to determine SI etiology at baseline. Patients with no clear SI etiology after workup were classified as cryptogenic. Imaging studies of patients with cryptogenic SI were manually reviewed by an abdominal radiologist to identify possible etiology.
The study exposure was the type of antithrombotic therapy defined as the prescribed antithrombotic regimen at discharge from hospitalization for the index SI, and classified as follows: none; anticoagulation (AC) only; antiplatelet (APT) only; AC & APT. AC was defined as intermediate or full dose AC. Prophylactic dose AC was classified as no AC. The primary outcome was arterial thromboembolism (ATE; acute coronary syndrome, ischemic stroke; transient ischemic attack; systemic embolism including recurrent SI) or venous thromboembolism (VTE) during 12-month follow-up. The cumulative incidence of the primary outcome over 12 months and corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI) was calculated for each antithrombotic therapy group and a Cox proportional hazards model was used to calculate hazard ratios (HR), with death as a competing risk.
Results: The eligibility criteria were met by 255 patients. The median age was 66 years and 130 (51%) were female. At least one cardiovascular risk factor was present in 221 (87%) patients. while 44 (17%) had previously diagnosed atrial fibrillation. 30 (12%) patients had prior VTE and 83 (33%) had acute concurrent ATE or VTE diagnosed at another site during hospital admission for the index SI.
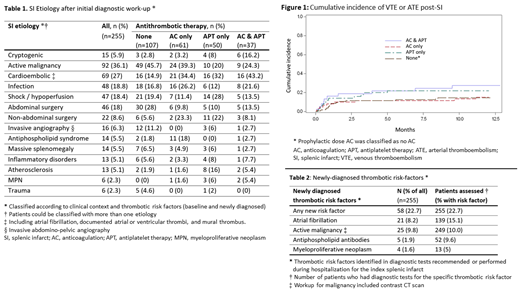
The SI etiology after initial diagnostic work-up, stratified for type of antithrombotic therapy at hospital discharge, is shown in Table 1. The most prevalent presumed etiologies were active malignancy in 92 (36%), cardioembolic in 69 (27%), infection in 48 (19%), shock/hypoperfusion in 47 (18%) and abdominal surgery in 46 (18%). Myeloproliferative neoplasms (2%) and antiphospholipid syndrome (6%) were rare causes. Only 15 cases (6%) were cryptogenic. Radiology review identified a possible etiology that was missed on initial review in 5 (33%) of the 15 cryptogenic SI's. These etiologies were cardioembolic [n=3], infectious [1] and malignancy [1].
Diagnostic work-up post-SI led to identification of a previously undiagnosed thrombotic risk factor in 58 cases (23%), especially atrial fibrillation (8%) and malignancy (10%), as shown in Table 2. The yield of antiphospholipid antibody testing was 10%, after confirmatory testing (Table 2).
148 patients (58.0%) were discharged from hospital with antithrombotic therapy (Table 1). The overall 12-month cumulative incidence of ATE or VTE was 18% [95% CI 13.5-23%]. Figure 1 shows the cumulative incidence of VTE or ATE stratified for type of antithrombotic therapy. The APT only and AC & APT groups had the highest 12-month incidence of ATE/VTE (22% [11.7-34.4%] and 27.4% [14.1-42.6%], respectively). In the cryptogenic SI group, 9 (60%) received AC and 4 (27%) patients had ATE/VTE.
Conclusions: SI is associated with a wide spectrum of clinical disorders. Cryptogenic SI is rare and imaging review may identify possible etiologies in such cases. Diagnostic workup leads to identification of new thrombotic risk factors in 1 in 4 patients and should be pursued. The rate of ATE or VTE at 12-months post-SI is high despite antithrombotic therapy. Further research is needed to identify the optimal antithrombotic therapy in these patients.
Leader: Leo Pharma: Honoraria; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Bayer: Honoraria; Sanofi: Honoraria.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal